TreeviewCopyright © aleen42 all right reserved, powered by aleen42
Project Scope Management Back
1. Definition
- Scope refers to all the work involved in creating the products of the project and the processes used to create them.
- A deliverable is a product produced as part of a project, such as hardware or software, planning documents, or meeting minutes(會議紀要)
- Project scope management includes the processes involved in defining and controlling what is or is not included in a project
2. Processes
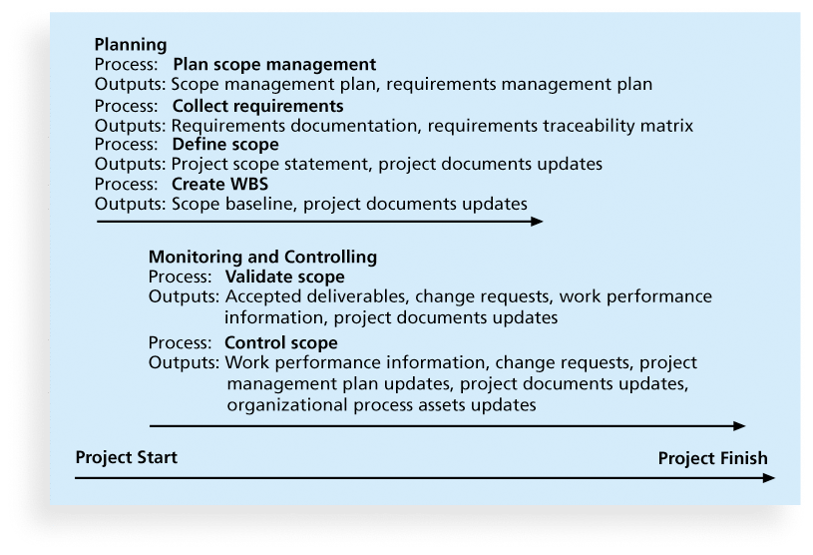
- Plan scope management
- To use expert judgment to develop the scope management plan.
- Collect requirements
- To use expert judgment to develop the requirements management plan.
- For some IT projects, it is helpful to divide requirements development into categories called elicitation(抽出), analysis, specification, and validation.
- It is important to use an iterative(迭代的) approach to defining requirements since they are often unclear early in a project.
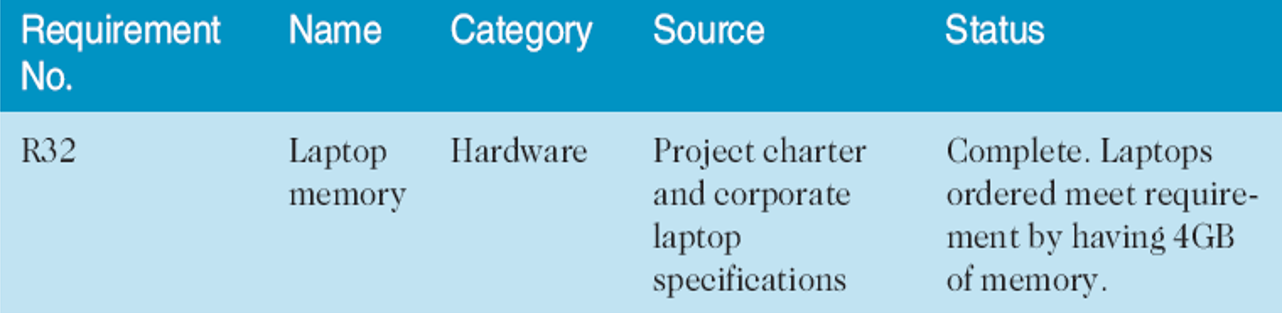
- A requirements traceability matrix (RTM, 需求追溯模型) is a table that lists requirements, various attributes of each requirement, and the status of the requirements to ensure that all requirements are addressed.
- Define scope
- Project scope statements should include at least a product scope description, product user acceptance criteria(用戶接受標準), and detailed information on all project deliverables.

- Project scope statements should include at least a product scope description, product user acceptance criteria(用戶接受標準), and detailed information on all project deliverables.
- Create WBS
- A Work breakdown structure(WBS) is a deliverable-oriented grouping of the work involved in a project that defines the total scope of the project.
- Decomposition(分解) is subdividing(細分) project deliverables into smaller pieces.
- A work package(工作包) is a task at the lowest level of the WBS.
- The scope baseline includes the approved project scope statement and its associated WBS and WBS dictionary.
- Validate scope
- Scope validation involves formal acceptance of the completed project deliverables. (Acceptance is often achieved by a customer inspection and then sign-off on key deliverables)
- Control scope
- Scope control involves controlling changes to the project scope.
- Variance is the difference between planned and actual performance.
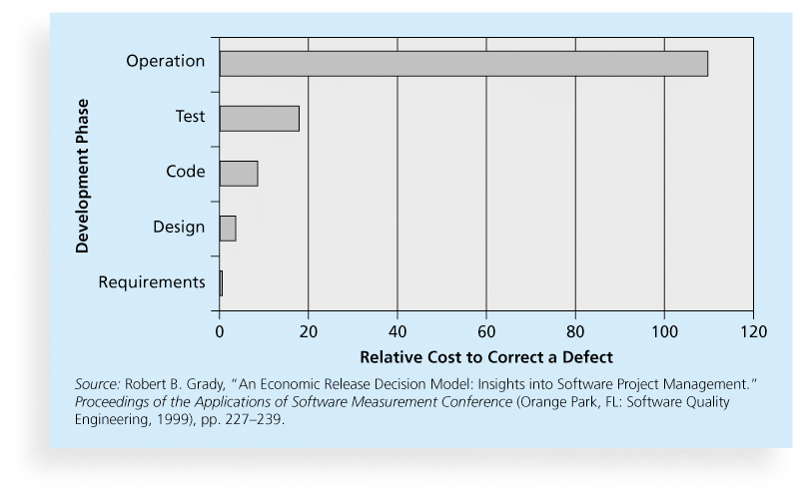
2. Cost of correcting
3. Approaches to develope WBS
- Analog approach(類比法): Review WBSs of similar projects and tailor to(適應) your project.
- Top-down approach(自上而下法): Start with the largest items of the project and break them down.
- Bottom-up approach(自底向上法): Start with the specific tasks and roll them up.
- Mind-mapping approach: a technique that uses branches radiating out(分流) from a core idea to structure thoughts and ideas.
4. WBS Dictionary
- A WBS dictionary is a document that describes detailed information about each WBS item.

5 Q&A
- What involves defining and documenting the features and functions of the products produced during the project as well as the processes used for creating them?
- Collecting requirements
- Controlling scope
- Defining scope
- Validating scope
answer: Collecting requirements.
- What documents how project needs will be analyzed, documented, and managed.
- requirements traceability matrix
- WBS
- requirements management plan
- project scope statement
answer: requirements management plan.
- Generating ideas by comparing specific project practices or product characteristics to those of other projects or products inside or outside the performing organization is known as what?
- variance
- prototyping
- benchmarking
- decomposition
answer: benchmarking.
- Which is a deliverable-oriented grouping of the work involved in a project that defines the total scope of the project?
- project charter
- project scope statement
- business case
- work breakdown structure
answer: WBS.
- Which should list and describe all of the deliverables required for the project?
- project charter
- WBS
- scope statement
- Gantt chart
answer: scope statement.
- What refers to the process of developing a working replica of the system or some aspect of the system?
- Prototyping
- Decomposition
- Variance
- Use case modeling
answer: Prototyping.
As the plugin is integrated with a code management system like GitLab or GitHub, you may have to auth with your account before leaving comments around this article.
Notice: This plugin has used Cookie to store your token with an expiration.